题库 / EAOfficialPractice-MSR-55
Discussion
The frequency of flooding onto floodplains—the lands situated adjacent to rivers and other waterways—depends on factors such as climate, drainage area, channel slope, and the absorptive capacity of soil. In rainy regions, the floodplain may be inundated frequently, and in arid regions the floodplain may remain dry for years. In many regions, floods occur primarily during the snowmelt runoff season.
Floods are often described in terms of their statistical frequency. A 100-year flood, for example, describes the level of floodwater expected to be equaled or exceeded once every 100 years. Such a flood is also considered the 1% annual exceedance probability flood (i.e., a flood with a 1% chance of being equaled or exceeded in any given year). Hydrologists commonly map the boundaries of 100-year floods to advise public officials on flood risk management and containment strategies.
Table of Waterway Statistics
The table shows the results of hydrologists’ measurements of all of the waterways in Region X under the hydrologists’ jurisdiction. Channel slope is the difference in elevation between two points on a waterway divided by the horizontal distance between them. Drainage area is the total surface area, upstream from the mouth of that waterway, from which water will drain to that point.
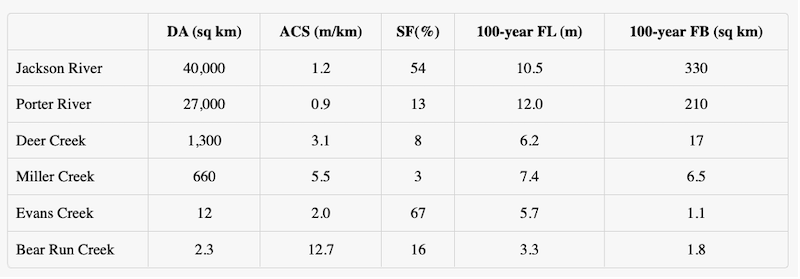
DA = drainage area (square kilometers)
ACS = average channel slope (meters per kilometer)
SF = snowmelt floods (% of total floods)100-year
FL = 100-year flood level (meters)100-year
FB = area within the 100-year floodplain boundary (square kilometers)
For each of the following, select Yes if it is explicitly mentioned in the passage (Discussion) but not in the table. Otherwise select No.
| YES | NO | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Snowmelt flooding
|
|
|
|
Absorptive capacity of soil
|
|
|
|
Drainage area
|