题库 / EAOfficialPractice-MSR-88
Designs
A certain electric utility is considering exactly two designs (Designs 1 and 2) for a new power generation plant. Each design would result in a plant that would generate the same amount of power annually; but Design 1 would use a single Type A power generator, whereas Design 2 would use three Type B power generators.
Type A generators cost less than Type B generators to fuel per unit of power generated and vent through taller chimneys, which better prevent pollutants from concentrating near the plant. However, Type A generators produce solid waste that is difficult and expensive to dispose of safely.
Type B generators produce no solid waste and, as compared to Type A generators, vent approximately half as much Pollutant X, and even less Pollutant Y, per unit of power generated annually. However, Type B generators vent through much shorter chimneys.
Pollutants by Phase
Both Type A and Type B generators emit (vent) significantly more of Pollutant Y during the startup phase—when a generator is brought to its normal power-generating phase from nonoperation. During startup, unhealthy levels of Pollutant Y can become concentrated at ground level near the power plant. The following table shows, for a single Type A or Type B generator, Pollutant Y emissions, in kilograms per hour (kg/hr), and the resultant contributions from those generators to the ground-level concentration of Pollutant Y, in micrograms per cubic meter of air (mcg/m3), near the plant during the startup and normal generating phases.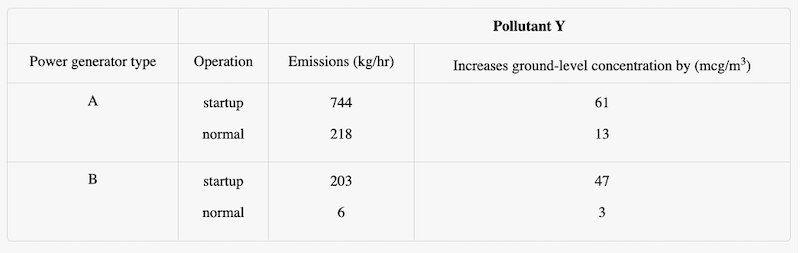
Suppose that the startup phase for Type A generators takes exactly one hour. Given this and based on the information in the tabs, which one of the following would be closest to the startup time, in hours, for Type B generators that would result in equal emissions of Pollutant Y for both power plant designs during a single startup phase?
3.67
0.27
0.81
1.22
36.33